The digital transformation, driven by cloud computing, has ushered in new possibilities, including enhanced scalability and streamlined operations. These capabilities have proven to be a significant boon for businesses, leading to substantial increases in productivity and return on investment. In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, maintaining a competitive edge in the cloud has become imperative for the successful operation of organizations.
In 2022, public cloud services were utilized by 76% of individuals, marking a substantial increase from the 56% reported in 2021 (source: Google).
However, this increased reliance on cloud services has also exposed organizations to a wave of intricate security threats that target cloud service providers. These threats exploit the limited visibility organizations have over data access and movement within cloud environments. Failing to implement preemptive measures to strengthen cloud security exposes organizations to substantial governance and compliance risks. This is especially concerning when dealing with sensitive client information, regardless of its storage location. Therefore, immediate action is vital for organizations to address these security challenges and ensure the safeguarding of their digital assets in the cloud.
Cloud Security: A Real-World Perspective
The primary focus of cloud security is to fortify the safety of all assets housed within cloud infrastructures, including sensitive data, applications, and services. Maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data as it interacts with the cloud is of paramount importance. Furthermore, the nature of cloud security is far from uniform, as each organization’s cloud environment is a unique blend influenced by factors such as industry, geographic location, and the specific architecture of their cloud setup, whether it be single, multiple, or hybrid.
Understanding these nuances is pivotal in crafting a precise security approach. For instance, businesses dealing with highly regulated data, such as those in healthcare or finance, must adhere to stringent compliance standards. Geography plays a role too, as data sovereignty laws differ across borders, affecting data storage and processing.
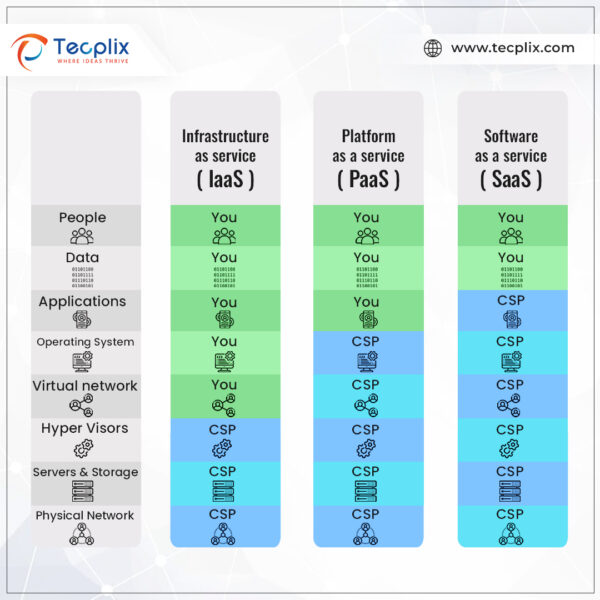
Shared Responsibility in the Cloud
Moreover, the choice between a single, multiple, or hybrid cloud infrastructure significantly impacts the security strategy. Hybrid environments, which combine public and private clouds, introduce additional complexity. A comprehensive strategy must account for these intricacies.
In conclusion, cloud security isn’t a one-size-fits-all endeavor. To achieve robust protection, it’s essential to tailor the approach, considering the unique needs, challenges, and regulatory demands of your organization’s cloud ecosystem.
Top Cloud Vulnerabilities

Cloud Misconfigurations
Cloud misconfigurations can manifest in various ways, a few of which we’ll explore below:
a. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Inadequate identity and access management (IAM) occurs when a user or service in your infrastructure has access to resources they shouldn’t or don’t need access to. To mitigate this risk:
- Adhere to the principle of least privilege, avoiding over-granting permissions
- Utilize third-party tools for scanning and detecting IAM policy misconfigurations
- Regularly review access and privileges as they evolve over time
b. Public Data Storage
When data repositories, such as S3 buckets or occasionally SQL databases, are partially or entirely accessible to the public, this misconfiguration can result from errors in resource settings. To minimize this threat:
- Employ third-party tools to scan your infrastructure and promptly detect such vulnerabilities
- Always configure your data storage to be private by default in your cloud resources
- When using infrastructure-as-code frameworks, ensure that the code is reviewed by another team member
Insecure APIs
APIs play a pivotal role in contemporary software development, serving in microservices, application, and website backends, and handling requests from a variety of sources. Malicious requests can assume various forms, with some common examples being code and query injection, exploiting poor access controls, and targeting vulnerabilities in outdated components like software libraries, database engines, or runtime environments. While many cloud providers offer in-house solutions, you can take several independent steps to secure your APIs:
- Deploy a web application firewall (WAF) to filter requests based on IP addresses and HTTP header information, and to detect code injection attacks
- Set response quotas and other metrics per user
- Implement DDoS protection
Lack of Visibility
As organizations operate thousands of cloud instances, maintaining visibility into the entire infrastructure is crucial. Lack of visibility can lead to delays in identifying and addressing threats, potentially resulting in data breaches. To address this, organizations should:
- Continuously monitor and detect potential threats
- Ensure comprehensive visibility into your cloud infrastructure
- Implement tools like a CNAPP to reduce risk and expedite response times in case of a breach
Lack of Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification to access accounts or data. To mitigate this risk:
- Implement and mandate MFA for all employees granted cloud access to their accounts and data
Malicious Insiders
Unauthorized access to your company’s cloud resources can occur through various means, including loose access rules or former employees retaining valid credentials. Malicious insiders can also exploit account hijacking resulting from successful phishing attacks or weak credential security. This poses a significant threat to data and intellectual property. To minimize this threat:
- Ensure MFA is active
- Employ automated tools to filter out phishing emails
- Educate employees about phishing attacks
- Enforce secure password practices
Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks (DDoS)
DDoS attacks aim to disrupt web services by overwhelming servers with requests from multiple sources. To mitigate this threat:
- Choose a cloud provider equipped to protect against DDoS attacks, and ensure that DDoS protection on your cloud service is consistently enabled
Cyber Threats from APT Groups and Organized Crime
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups have emerged as formidable adversaries, primarily targeting valuable data. As a proactive measure, organizations should conduct red-team exercises to identify any APT presence on their networks. Minimizing APTs involves:
- Conducting a comprehensive business impact analysis to assess the value of your information assets
- Actively participating in cybersecurity information-sharing groups to stay informed
- Familiarize yourself with relevant APT groups and their techniques
- Engaging in offensive security exercises to simulate APT group tactics
- Fine-tuning your security monitoring tools to detect APT tactics effectively
Cloud Security: Architecture and Strategy
While businesses rush to harness the power of the cloud, they must not overlook the critical aspects of security. The situation can become even more complex when multiple cloud providers are in the mix. In such cases, security professionals need to carefully consider the combination of default cloud controls, premium controls, and third-party security solutions to address their unique risk profiles, which can vary at the application level. Key takeaways for effective cloud security architecture and strategy include:
- Aligning cloud services and infrastructure decisions with your business objectives, risk assessment, security threats, and legal compliance
- Developing a well-defined infrastructure strategy
- Embracing due diligence and vendor security assessments, along with secure design and integration practices to prevent systemic failures
Misconfigurations and Threats in Serverless and Container Environments
As organizations increasingly turn to serverless and containerized workloads for application deployment, it’s essential for organizations to focus on enhancing their cloud hygiene practices, application security, observability, access control, and secrets management. This not only reduces the attack surface but also mitigates the blast radius of potential security incidents. Key takeaways for managing serverless and container workloads effectively include:
- Implementing cloud security posture management (CSPM), Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM), and cloud workload protection platforms to enhance visibility and enforce compliance
- Investing in cloud security training, establishing robust governance processes, and adopting secure cloud architecture patterns to minimize the risks associated with insecure cloud configurations
- Prior to migrating to serverless technologies, development teams should prioritize robust application security and engineering best practices, ensuring the removal of traditional security controls doesn’t lead to vulnerabilities
Cloud Security Best Practices

Select a Trustworthy Cloud Service Provider
The initial step in safeguarding your data involves selecting a trustworthy cloud service provider. The selected provider should offer secure data storage, encryption, and access controls. Look for providers adhering to relevant security standards and regulations, such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Comprehend Your Security Responsibilities
Understanding the division of responsibilities is crucial when migrating data to cloud services. Typically, cloud providers secure the infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing the data stored on that infrastructure. It’s imperative to be aware of your responsibilities and take necessary actions to protect your data.
Utilize Robust Authentication Methods
While passwords serve as the initial line of defense against unauthorized access, they are susceptible to theft, leaks, or compromise. Implement strong authentication methods, such as multifactor authentication, to significantly mitigate the risk of unauthorized data access.
Deploy Encryption
Encryption is a critical component of cloud security that ensures only authorized users can access encoded data. Implement encryption for both data in transit and data at rest to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Safeguard Data Throughout Its Journey
An ongoing challenge for businesses is identifying the whereabouts of sensitive data. Solutions facilitate the scanning of data at rest across multiple applications and locations, ensuring the discovery of sensitive data. Identifying data is only the first step; safeguarding it involves applying measures such as encryption, access restrictions, and visual markings.
Implement Access Control
Effectively restrict access to sensitive data within cloud services by implementing access controls. These controls should adhere to the principle of least privilege, granting users only the minimum access required for their tasks. Role-based access control is a valuable tool for assigning roles and permissions based on job responsibilities.
Monitor Cloud Activity and Assess Security Position
Vital for detecting and preventing unauthorized access to data is regularly monitoring cloud activity. Cloud service providers offer monitoring services that can alert administrators to suspicious activities. Consistently reviewing cloud logs and audit trails helps uncover potential security threats.
Ensure API Security
Secure APIs are essential for accessing cloud services, as they can be vulnerable to attacks if not properly protected. Implement secure APIs with strong authentication and encryption to prevent unauthorized access to cloud services.
Conduct Routine Security Evaluations
Regular security assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and evaluating the effectiveness of security measures. These assessments can be carried out internally or by third-party security experts.
Educate Your Workforce
Ensure that your employees are knowledgeable about the security risks associated with storing data in cloud services and train them in best practices for data security.
Implement the Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust is a security strategy encompassing a set of principles aimed at enhancing security. These principles include verifying explicitly, utilizing least privilege access, and assuming a breach.
Enhance Cloud Security Posture
Cyber threats persist 24/7, and it’s imperative for organizations to maintain constant vigilance over their network infrastructure. Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) offer round-the-clock cybersecurity services along with a range of additional benefits. Outsourcing cybersecurity responsibilities can yield various advantages, but it’s important to recognize that not all MSSPs are the same. The MSSP landscape is oversaturated, making the process of finding the ideal provider a time-consuming endeavor.
MSSP for a Safer Cloud Journey
Tecplix possesses extensive expertise in cybersecurity and has exhibited unwavering responsiveness consistently. We are committed to continuously monitoring the digital landscape to proactively mitigate threats, ensuring minimal to no disruption to daily business operations. Through our Managed Security Services, we safeguard organizations throughout their cloud migration journey and beyond.

Tecplix Cloud Security Coverage
What You Get:
Real-time Threat Detection and Response: Tecplix delivers real-time threat detection and immediate response, which is essential for effective threat intelligence. Tecplix provides round-the-clock monitoring to proactively manage and mitigate security incidents.
Advanced SOC: Tecplix offers Security Operations Centers (SOCs) for safeguarding essential infrastructure, including servers, applications, databases, and networks. An around-the-clock SOC is an indispensable component of any advanced cybersecurity strategy.
Access to Expertise: Tecplix grants organizations access to highly certified professionals. Tecplix typically employs experienced engineers who hold prestigious security certifications such as CCSK, CCSP, CISSP, and more, ensuring that your cybersecurity benefits from expert knowledge.
Meeting Compliance Standards: Achieving cybersecurity compliance with industry standards becomes a streamlined process when partnering with Tecplix. Certain regulatory laws like PCI, GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA demand a specific level of granular control and security. Tecplix guides you through the validation processes, helping you meet compliance goals and ensuring that your data and its privacy align with defined compliance requirements.


