In today’s digital landscape, businesses confront a multitude of cybersecurity threats that can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data. To confront these threats establishing a robust Enterprise Security Architecture (ESA) becomes essential for resilience. This blog delves into the critical elements of an effective ESA, offering a roadmap for identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks.
Understanding Enterprise Security Architecture
Building a resilient security framework hinges on grasping the layers comprising Enterprise Security Architecture:
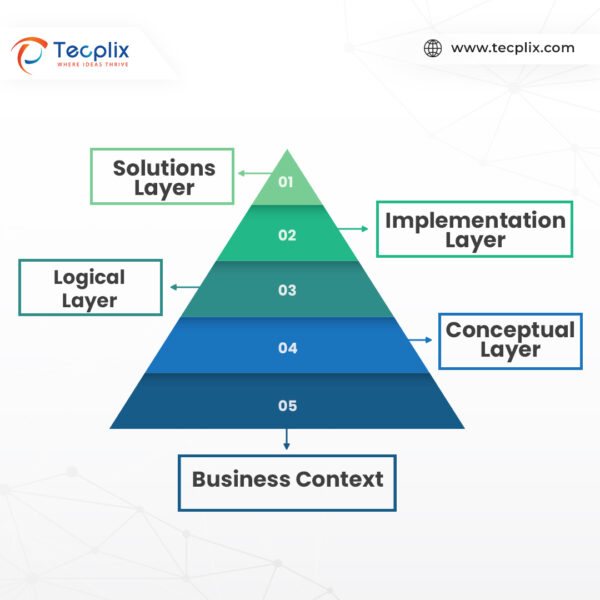
Layers of Enterprise Security Architecture
- Business Context: Aligning security initiatives with organizational goals ensures strategic security investments.
- Conceptual Layer: Establishing guiding principles and standards lays the groundwork for implementation.
- Logical Layer: Identifying assets requiring protection provides a comprehensive security overview.
- Implementation Layer: Detailing specific technologies and controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, secures the environment.
- Solutions Layer: Outlining tools and processes, like SIEM systems, manages security risks and incidents.
Managing Security Risks: A Four-Step Process
Effectively managing security risks necessitates a systematic approach comprising four key steps:
Risk Identification:
- Proactively identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses.
- Employ risk assessment methodologies and vulnerability scanning tools.
- Prioritize risks based on likelihood and potential impact.
Risk Assessment:
- Analyze the severity of each identified risk, considering its impact on operations, financial stability, and reputation.
- Categorize risks based on severity and likelihood for focused mitigation efforts.
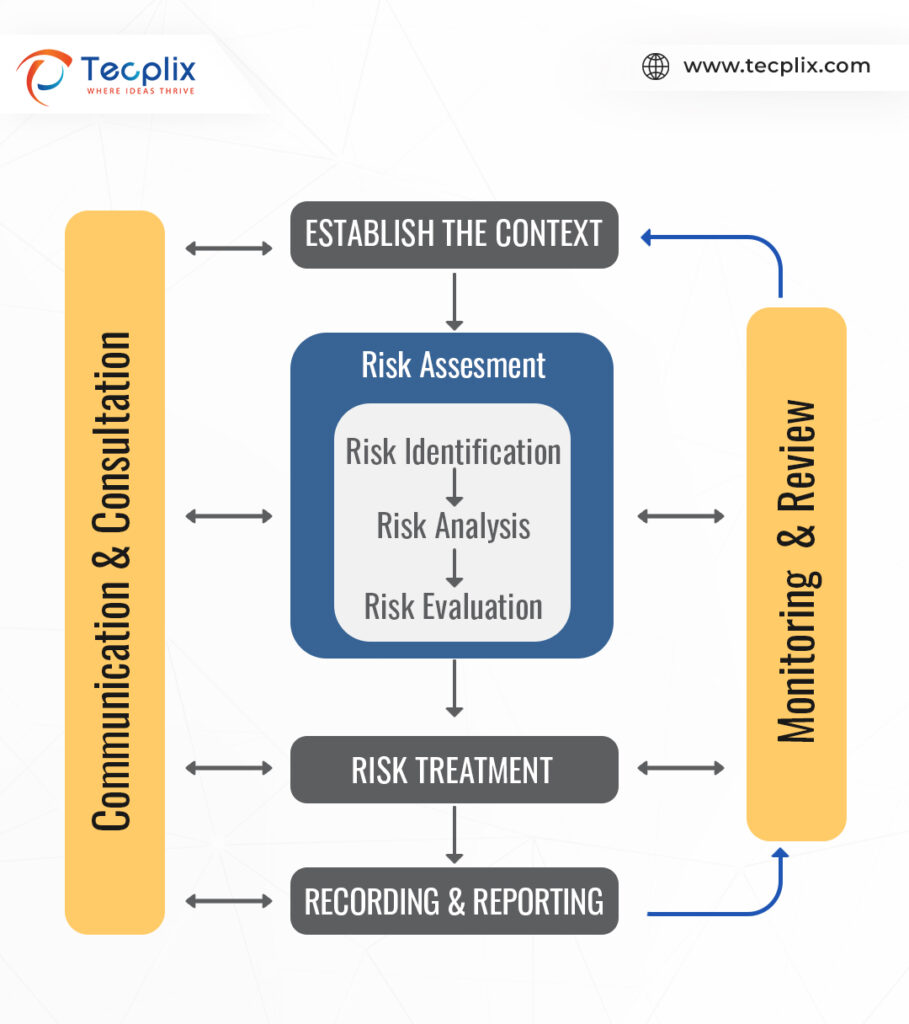
Managing Security Risks
Risk Treatment:
- Develop tailored controls, leveraging technical, administrative, and physical measures.
- Implement security controls like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Establish administrative and procedural controls to foster a security-centric culture.
Risk Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor the security environment for emerging threats.
- Utilize security monitoring tools like SIEM systems for real-time analysis.
- Regularly review and update the risk management framework.
Strategies for Effective Risk Management
To enhance risk management endeavors, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
Develop a Comprehensive Risk Management Framework:
- Establish a structured approach with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
- Implement standardized methodologies for consistency and transparency.
Align Security with Business Goals:
- Integrate security into business planning and decision-making processes.
- Allocate resources based on alignment with strategic business objectives.
Implement Layered Security:
- Utilize a multi-layered approach combining technical, administrative, and physical controls.
- Prioritize critical assets and implement stringent controls for their protection.
Promote a Culture of Security:
- Foster security awareness and accountability within the organization.
- Provide regular security training for employees.
- Encourage open communication and reporting of security incidents.
Continuously Improve:
- Regularly review and update security architecture.
- Conduct security audits and penetration testing.
- Stay informed about emerging cybersecurity trends.
Ensuring Proactive Enterprise Security Architecture
- Identify and Assess: Regularly evaluate systems and prioritize threats based on likelihood and impact.
- Implement Controls: Employ strong authentication, data encryption, network segmentation, and vulnerability patching.
- Monitor and Respond: Continuously monitor systems for suspicious activity and establish incident response plans.
- Maintain Architecture: Educate employees, conduct audits, update security measures, and integrate with business processes.
- Adapt and Improve: Allocate resources based on risk assessment, automate tasks, consider cloud solutions, and secure supply chains.
In conclusion, managing security risks within enterprise architecture demands a proactive and ongoing effort. By comprehending the layers of Enterprise Security Architecture and following a systematic four-step process, organizations can bolster their defenses. Implementing effective risk management strategies, aligning security with business objectives, fostering a culture of security, and embracing continuous improvement are pivotal in fortifying security frameworks. By adhering to these principles, organizations can mitigate the risk of security incidents, safeguard sensitive data, and ensure enhanced business continuity amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges.
Enhance Your ESA Security with Tecplix’s Expert Services
Beyond the comprehensive ESA security management approach outlined above, Tecplix offers a range of expert services to further fortify your security posture:
- Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing
- Security Architecture Design and Implementation
- Managed Security Services
- Security Awareness Training
- Incident Response and Forensics Services
- Compliance Audits and Consulting
Leverage Tecplix’s comprehensive security solutions and expert services to achieve the highest level of security for your ESA. Contact Tecplix today to learn more and discuss your specific security needs.